Key Takeaways
- NLP is the science and methods behind teaching computers to read, process, and understand language.
- LLMs = giant AI models built using that toolbox, specialized in generating new text at scale.
- NLP powers everyday tools like spam filters, voice assistants, and translation apps.
- LLMs (e.g., GPT-5, Claude, Gemini, Code Llama) are driving the new wave of content generation, keyword clustering, and coding automation.
- SEO tools (e.g., Yoast, Clearscope) rely heavily on NLP for keyword analysis and content scoring.
- Both work together: NLP interprets intent; LLMs scale the response.
When people throw around terms like NLP and LLM, it’s easy to think they mean the same thing. They don’t.
The confusion around NLP vs LLM is everywhere, from boardrooms to Twitter debates. Let’s clear it up. NLP and LLM come down to scope and function: Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the broad field that makes machines understand human language, while Large Language Models (LLMs) are one of its most powerful offspring, designed to generate human-like text at scale.
Let’s cut the noise and break down the differences, similarities, and real-world use cases—so you’ll never mix them up again.
Understanding the difference is not just a tech exercise. For anyone in SEO or content marketing, it’s about knowing how Google interprets search queries, why AI tools draft articles so convincingly, and how you can leverage both technologies to stay ahead.
If you’re wondering how this impacts SEO, marketers, and even coders—keep reading.
All in all, knowing where NLP ends and where LLMs begin helps you see not only how Google ranks pages but also how your favorite AI writing assistants actually work.
LLM vs NLP: Key Differences
Marketers love quick comparisons, so let’s start with the essentials. NLP, or Natural Language Processing, is the broader discipline that covers tasks such as parsing grammar, analyzing sentiment, and understanding intent. LLMs, or Large Language Models, are advanced systems within NLP. They are trained on massive datasets—often trillions of words—and are designed not only to interpret language but also to generate entirely new content, from blog posts to computer code.
Here’s a simple NLP vs LLM comparison table that highlights the key differences in scope, function, and real-world uses:
| Aspect | NLP | LLM |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad AI field for human–computer language interaction | Subset of NLP, focused on large-scale text generation |
| Core Function | Interpret, classify, or transform text | Generate coherent, human-like text and code |
| Techniques | Linguistics, rule-based models, ML | Transformers, neural networks, deep learning |
| Data Scale | Small → medium datasets | Trillions of words, massive corpora |
| SEO Role | Intent detection, entity extraction, keyword relevance | Content scaling, blog drafts, FAQs, schema generation |
| Examples | Google’s RankBrain, spam filters, translation tools | ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Code Llama |
As can be seen, NLP provides the foundation, while LLMs demonstrate what happens when that foundation is scaled to the extreme. NLP underpins core functions such as search, sentiment analysis, and voice recognition, whereas LLMs extend these capabilities into text generation, intelligent assistants, and large-scale automation.
What is NLP?
Natural Language Processing, or NLP, is essentially the toolkit that lets computers make sense of human language. Instead of being one single algorithm, it’s an entire field built from linguistics, computer science, and machine learning techniques. The aim isn’t just technical—it’s about making interactions with machines feel closer to real conversation.
Take search as an example. When you type “Apple” into Google, NLP helps the engine figure out whether you’re looking for fresh fruit or the tech giant. The same principle applies in SEO—this technology also powers keyword clustering, content scoring, and even readability checks in tools like Yoast or Clearscope. These platforms rely on NLP to analyze sentence flow, keyword usage, and overall clarity—helping writers create copy that’s easier to read and better optimized.
Consequently, NLP is the invisible force behind semantic search and modern SEO. If NLP weren’t part of the picture, search engines would miss the point of most queries—and marketers would still be relying on outdated keyword stuffing tactics from the early 2000s.
SEO examples of NLP in action:
- NLP tells Google whether “Tesla” is about the car company or the inventor.
- Yoast SEO plugin checks readability and keyword density using NLP techniques.
- Tools like Clearscope and MarketMuse rely on NLP to score how well your content covers a topic.
So, does NLP come under LLM? Certainly not. NLP is a broad discipline, and LLMs are its most advanced offspring.
Ultimately, when you see “semantic SEO” or “search intent analysis,” you’re seeing NLP at work.
What is LLM?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are neural networks trained on massive datasets—billions or trillions of words. Their job? To predict the next word in a sequence so well that the output reads like it came from a human.
At their core, Large Language Models work by predicting what word should come next. When they get it right consistently, the result isn’t just a neat sentence—it can be an entire blog draft, a convincing sales email, or even a block of usable code.
Some of the best-known examples are GPT-5 (the engine behind ChatGPT), Claude, Google’s Gemini, and Code Llama, which is geared toward developers.
In SEO and content marketing, LLMs are already reshaping workflows. They can generate blog post outlines, draft product descriptions, propose FAQ sections designed to capture “People Also Ask” boxes, and even write meta descriptions at scale. Not only that, but some LLMs are specialized. Take Code Llama as an example. It’s among the top LLMs for coding and is already helping developers cut down on repetitive work and speed up debugging.
And of course, this sparks one of the most common questions: is ChatGPT an NLP tool or an LLM? It’s best understood as an LLM – powered by NLP techniques at its core.
Similarities between NLP and LLM
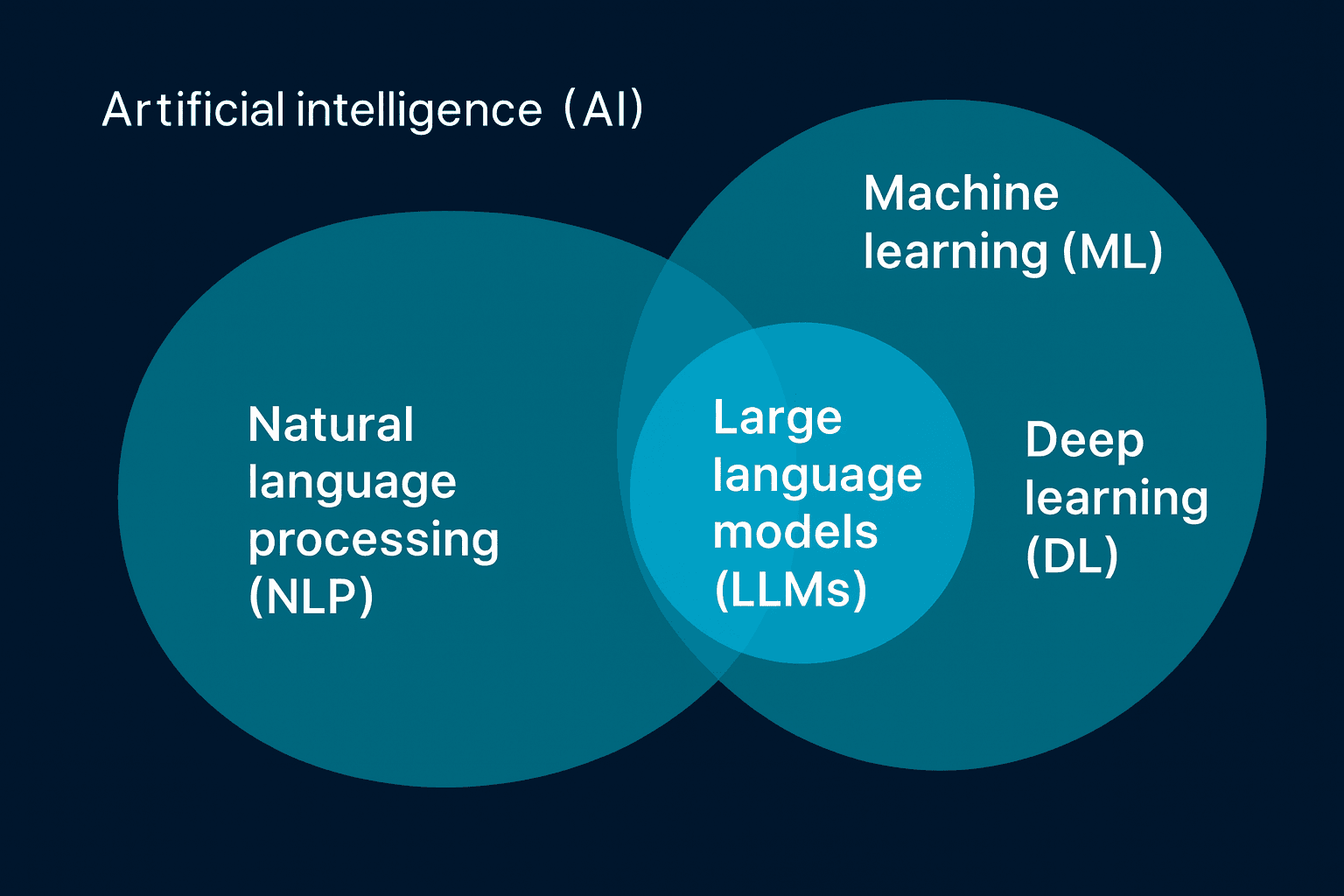
At the same time, it’s important to realize that LLMs and NLP share the same DNA. Both handle human language, both rely on data, and both aim to bridge communication between humans and machines. In fact, most LLMs wouldn’t function without the foundational methods developed in NLP, such as tokenization, parsing, and sentiment detection. The real distinction is scale: NLP is the field, LLMs are the massive, generative models within it.
What Are Examples of NLP and LLM?
Although both deal with language, the way they’re applied looks different.
Think of the last time Gmail warned you about a suspicious email. That’s NLP classifying spam. When Netflix recommends a movie and tags it with genres like “psychological thriller,” NLP is doing entity recognition. In SEO, NLP clusters keywords, extracts entities from top-ranking content, and analyzes sentiment in customer reviews.
NLP examples:
- Sentiment analysis for brand monitoring (e.g., scanning reviews to see if people love or hate your product).
- Keyword clustering and topic modeling for SEO.
- Voice recognition (Siri, Alexa).
- Translation (Google Translate).
By contrast, LLMs don’t just analyze—they create. Instead of simply labeling or classifying, they produce new text, code, and insights—often at a speed and scale that no human team could match.
LLM examples:
- Drafting long-form blog posts that editors refine.
- Creating FAQ sections optimized for snippets.
- Auto-generating schema markup or meta tags.
- Coding copilots (some of the top LLMs for coding—like GPT-5, Claude, and Code Llama—are changing how developers build and debug software).
Real-world Applications of NLP and LLM
Understanding the gap between NLP and LLM becomes easier once you see how they’re applied. In practice, both power everyday tools, though they do so in very different ways.
SEO and Content Marketing
- NLP:
- Google’s BERT update interprets query intent with NLP.
- Keyword clustering tools use NLP to group semantically related terms.
- LLM:
- Create blog drafts, meta descriptions, and social captions.
- Build briefs with headings and FAQs, driven by smart SEO data.
- Draft optimized alt-text and schema for large sites.
Business
- NLP: Automates email classification, detects spam, routes tickets in customer support.
- LLM: Drafts business proposals, creates personalized email campaigns at scale.
Healthcare
- NLP: Extracts conditions and prescriptions from unstructured doctor’s notes.
- LLM: Generates patient-friendly explanations of diagnoses.
Education
- NLP: Grades multiple-choice or short-text answers.
- LLM: Tutors students, explains concepts conversationally.
Why People Confuse NLP and LLM?
Given the overlap, it’s no surprise that people blur the terms. After all, both deal with language tasks, so the boundary isn’t always obvious. This is why the debate around natural language processing vs large language models keeps coming up. To make things more confusing, marketing hype hasn’t helped. Tech companies often throw around “AI” or “LLM” even when describing simple NLP features, just because it sounds cooler. Think of it this way:
NLP = the kitchen (recipes, tools, cooking methods).
LLM = a Michelin-star chef using that kitchen to create never-ending dishes.
Without the kitchen, the chef wouldn’t exist. But without the chef, the kitchen wouldn’t be as impressive.
Which raises a common question: Can LLM replace NLP? The answer is no. LLMs are part of NLP, not a replacement. Rule-based systems, small classifiers, and traditional NLP algorithms are still essential for lightweight tasks like spam detection or real-time translation.
What’s Next for NLP and LLMs
When it comes to the road ahead, NLP and LLMs aren’t splitting off—they’ll keep evolving together.
NLP is likely to evolve into a multimodal field, processing not only written text but also speech, visuals, and even video content. Think about how search engines are already moving beyond blue links into visual and conversational results (like AI Mode) —this trend depends heavily on NLP getting smarter. LLMs, by contrast, are expected to become smaller, faster, and more domain-specific. Instead of one giant model for everything, we’ll see specialized LLMs for law, healthcare, and yes—SEO.
That said, challenges remain. Hallucinations are still a problem—LLMs sometimes invent facts. Bias in training data continues to influence outputs. And the computing costs of building giant models are staggering.
It’s also worth placing NLP and LLMs back into the bigger picture: machine learning (ML). Machine Learning drives everything from Netflix recommendations to bank fraud alerts. NLP is one branch within that bigger field, focused only on language. That’s why people often ask: NLP or ML, which is better? The truth is, neither. Natural Language Processing is built on Machine Learning, and Large Language Models are built on NLP. They’re not rivals—they’re layers in the same AI pyramid.
NLP and LLM in Everyday SEO
For SEO professionals, the impact is already visible. With NLP, Google deciphers intent, connects entities, and delivers search results that make sense to the user’s question. Without NLP, semantic search, entity-based optimization, and SERP visibility strategies wouldn’t exist.
LLMs, however, are the tools marketers now use to scale content. They generate first drafts, expand keyword coverage, suggest FAQs, and even propose structured data for featured snippets. If NLP is what makes Google smart, LLMs are what make your SEO team faster.
Accordingly, modern SEO is no longer about choosing between NLP and LLM. It’s about blending them—NLP to understand the landscape, LLMs to create content that fills it.
- NLP in SEO → powers intent detection, SERP analysis, and entity recognition, ensuring your content aligns with what search engines expect.
- LLMs in SEO → accelerate production by drafting optimized content, generating FAQs for “People Also Ask,” and even creating schema to boost visibility.
- Hybrid workflows → the real advantage comes from combining NLP insights with LLM outputs, allowing SEO teams to plan content strategically and scale execution efficiently.
Final Thought
Here is the bottom line: NLP gives machines the ability to understand us, and LLMs take that foundation and push it to the next level. When Google nails your search intent or Grammarly cleans up your copy, that’s NLP in action. And when ChatGPT drafts a blog outline or Code Llama autocompletes a block of code, that’s an LLM taking things to the next level.
For SEO and content marketing, this distinction matters. NLP ensures your content aligns with search intent. LLMs help you produce content at scale without sacrificing quality. Neither replaces the other—they’re a tag team shaping how we search, write, and code today.
NLP is the strategist, LLMs are the executioners — together they’re rewriting how we search, create, and communicate online.




